Module 2. Underdevelopment Problematique
OBJECTIVES:
At the end of this module the student should be able to:
- Describe the “vicious cycle of poverty;”
- Characterize problems associated with underdevelopment;
- Describe the problematique technique; and
- Define subordinate and superordinate influential factors.
ACTIVITIES
Read Chapter 2 of your text. Perform the following:
Activity 2.1. Draw a problematique map of a problem situation in your community. Examples of these problems are: poor garbage disposal; drug abuse; lack of health care; beggars; poor water supply; poor roads. The important thing is to focus on only one problem. Activity 2.2. Identify the subordinate influential factors.
Activity 2.3. Identify the superordinate influential factors.
ANSWERS:
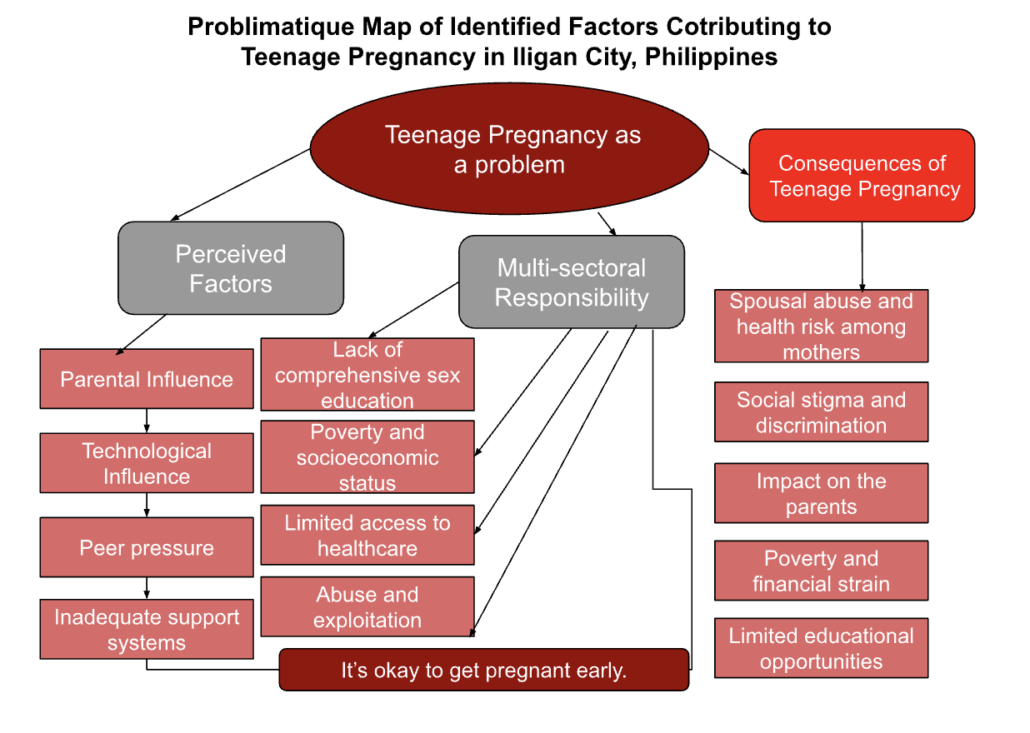
In the context of teenage pregnancy in the Philippines, there are both subordinate influential factors (sub-factors) and a superordinate influential factor (a broader factor that encompasses and influences the sub-factors).
| Subordinate Influential Factors | Superordinate Influential Factors |
Cultural and Religious Beliefs Peer Pressure and Influence Media Influence Early Marriage Gender Inequality Inadequate Support Systems Limited Access to Healthcare Abuse and Exploitation Educational Disadvantage | Limited access to education and information Lack of access to healthcare and contraception Early marriage due to economic pressures Increased likelihood of unsafe abortions Reduced opportunities for personal growth and development |
It’s important to recognize that these factors are interconnected and mutually reinforcing. Addressing teenage pregnancy in the Philippines requires a multifaceted approach that considers both the superordinate and subordinate influential factors, addressing poverty and its associated effects, while also targeting specific areas such as education, healthcare, and cultural attitudes toward early pregnancies.
MODULE 2 NOTES:
Complexity of Underdevelopment Problems:
- Problems associated with underdevelopment are complex.
- Analyzing them often results in short-term solutions.
Vicious Cycle of Poverty:
- Coined by Daniel Lerner in the mid-1960s.
- Describes a situation where economic progress is hindered by counter-tendencies, primarily excessive population growth.
- Diagram illustrating the vicious cycle includes lack of technology, low savings, unequal wealth distribution, malnutrition, and more.
Critique of the Vicious Cycle:
- Lerner’s analysis assumes individual and sequential arrival of problems.
- Underdevelopment problems are observed to be pervasive, interrelated, and recurrent.
- Introduction of the concept of “sustainable development.”
Problematique Method:
- Developed by Michael Molenda and Anthony Di Paolo in the late 1970s.
- Problematique refers to a complex cluster of recurrent problems.
- The technique involves identifying superordinate and subordinate influential factors through unstructured interviews.
- Example of Problematique Map:
- Lack of an advanced degree and poor economic policy are root causes.
- High cost of living and low income are symptoms.
- Diagram helps identify superordinate and subordinate influential factors.
Summary:
- Underdevelopment problems are intricate and interrelated.
- The vicious cycle of poverty and Lerner’s analysis criticized.
- Problematique method introduced for complex problem analysis.
- Problematique map serves as a visual tool for identifying root causes and symptoms.



